The Canadian Pain Society reports that 20% of all Canadians—one in five—suffer from chronic pain. Up to half of those people suffer from osteoarthritis, a disease which affects more than three million Canadians.
The staggering costs associated with lost productivity, related health conditions, and medical treatments amount to hundreds of billions of dollars each year. But in many cases, the wait times for treatment are the main obstacle for pain sufferers. Seeing a pain specialist in Canada often involves a wait time longer than a year. Three out of four people waiting for pain care say that their pain interferes with their work. Half suffer from depression. And 35% of people waiting report that they’ve considered suicide.
Over-the-counter drugs can only go so far in treating chronic arthritis pain. In addition, there are risks associated with relying on pain medication over a long-term period. That’s where alternative therapies come in. From acupuncture to nerve stimulation, the following nine treatment options may help you to find relief.

1. Topical gels, creams, and patches.
What are they? Topical treatments can be applied directly to the skin. They tend to include sodium channel blockers, such as prilocaine or lidocaine, as active ingredients. Prescription non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) that can be applied to the skin via a spray, patch, gel, or drops are also becoming more widely available.
How do they work? Sodium channel blockers numb the nerve endings close to the skin. Topical NSAIDs work by reducing the number of inflammation-causing proteins in joint fluid.
What conditions do they treat? Topical sodium channel blockers work best for pain caused by neuropathy. Topical NSAIDs work to treat pain and inflammation caused by arthritis.
Side effects: Topical NSAIDs are ideal because they’re applied locally to the area where it hurts. Unlike oral NSAIDs, absorption into the body is minimal and therefore they pose fewer risks for cardiovascular and gastrointestinal side effects. Side effects are usually at the site of application, including itching, irritation, or rash.
2. Flexible shoes.
What are they? Most people think they need special shoes to minimize the effects of arthritis on their knee joints. But a study conducted in 2010 indicated that flexible shoes such as sneakers and flip-flops are the best option for individuals suffering from osteoarthritis. Sneakers and flip-flops decreased the force on knee joints by 11-15% compared to special walking shoes or clogs.
How do they work? Force applied to knee joints is associated with an increased risk of pain. Flexible shoes reduce the force exerted on the joints.
What conditions do they treat? Osteoarthritis pain in the knees and possibly hips.
Side effects: Flip-flops have been associated with other issues, such as inflammation in the connective tissues at the base of the foot. They may also cause falls. A closed shoe with a flexible sole is optimal.
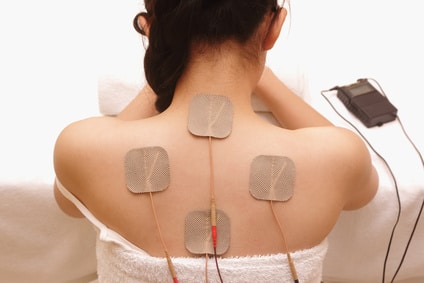
3. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)
What is it? TENS therapy involves using a handheld machine to send an electric current to pain sites via wires and electrodes attached to the skin.
How does it work? The electrical current cancels out pain signals and stimulates the nervous system, possibly even causing the brain to release endorphins, which relieve pain.
What conditions does it treat? Any form of chronic pain.
Side effects: TENS is not suitable for people who have a pacemaker, open wounds, or infection.
4. Meditation
What is it? Meditation is a mind-body relaxation technique that involves repetition of mantras, eliminating thoughts from the mind, focusing on bodily sensations or breath, or listening to guided imagery. It can help to reduce pain.
How does it work? Stress is a major factor in arthritis pain. When you’re stressed, it triggers the release of chemicals that cause inflammation. Relaxation techniques such as medication reduce stress, thereby reducing inflammation and pain. Meditation can also help you to cope with acute, intense pain.
What conditions does it treat? Any form of pain. Studies have found that meditating on a regular basis changes the brain’s normal response to pain.
Side effects: None.
5. Steroid injections.
What are they? Cortisol is a hormone found naturally in the body which targets inflammation. Steroids such as cortisone, prednisone, and hydrocortisone mimic the effects of cortisol.
How do they work? Steroid injections are given at the site of pain, usually a joint. They relieve pain and target inflammation.
What conditions do they treat? Any pain caused by inflammation, including inflammatory arthritis.
Side effects: Steroid injections should be given a maximum of three times per year, as their effects last for weeks and sometimes months. When given more often, they can weaken ligaments and tendons.
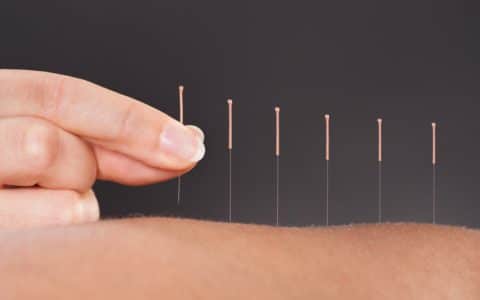
6. Acupuncture
What is it? Acupuncture is a therapy which comes from traditional Chinese medicine. It involves placing small needles at certain places in the body, called meridians, which allows the body to release trapped chi, a life energy.
How does it work? Studies have shown that acupuncture can stimulate the production of endorphins, the body’s natural pain relievers. Other research suggests that acupuncture may increase circulation to pain sites, which helps to remove chemical compounds that play a role in pain.
What conditions does it treat? Acupuncture can be used to treat any form of chronic pain, including arthritis pain.
Side effects: People who are taking blood thinners may be more likely to bleed during acupuncture. Those undergoing chemotherapy may be more susceptible to infection.
7. Hyaluronic acid injections.
What are they? Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a thick fluid found naturally in cartilage.
How do they work? Injections are used to treat cartilage that has suffered damage. Some research suggests HA even assists in cartilage regeneration, though other studies have found that its effects vary significantly from patient to patient. It may be given as a single injection or three to five separate injections. If successful, it may be repeated on a yearly basis.
What conditions do they treat? Hyaluronic acid injections can be used to help repair damaged cartilage in the knee joints. It is probably not suitable for juvenile arthritis.
Side effects: May cause an infection or allergic reaction in some patients.

8. Physiotherapy and exercise.
What is it? Physiotherapy treatment involves a series of exercises and stretches designed to strength muscles, improve posture and range of motion, decrease pain, and boost the patient’s energy, mood, and quality of life.
How does it work? Physiotherapy involves seeing a physical therapist one or more times per week. With the patient’s input, the physiotherapist develops a program of aerobic, stretching, and strengthening exercises, which patients are encouraged to complete during their session and at home.
What conditions does it treat? Any form of arthritis, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Side effects: Pain or injury may occur during physiotherapy.
9. Nerve block
What is it? A nerve block involves an injection of a local anesthetic and a steroid into a nerve. Nerve blocks can be used both to treat pain and to help doctors diagnose sources of pain.
How does it work? The anesthetic blocks nerve signals, while the steroid targets inflammation at the site of the tissues or joints.
What conditions does it treat? Nerve blocks are used to treat spinal pain, or pain in the limbs.
Side effects: Bleeding and infection. If the physician injects the nerve block at the wrong nerve site, it could disrupt movement or sensation in areas controlled by that nerve.
This page is also available in:
![]() English
English


